Google says it is working on it, but is still positioned to profit as local businesses claw back visibility with paid ads.
Google Maps carries approximately 11 million illegitimate local listings, with hundreds of thousands more getting created each month, the Wall Street Journal reported this week. These fake listings push real businesses further down the local search results, impacting their ability to reach customers and make unsuspecting users easy targets for scammers.
Google says it is aware of the problem and that it has plans to do more to combat spammers and scammers taking advantage of local listings. It’s not in the company’s interest to jeopardize user trust, yet as many marketers point out, it stands to profit as local businesses turn to paid ads to regain search visibility.
“Duress vertical” scams and spammy business names
First, a look at the problem. The majority of car repair, towing, electricians, contractors, attorneys, movers and other service categories aren’t located at the addresses shown in Google Maps, according to a survey of experts conducted by the WSJ. Internally at Google, the paper reprted, these categories are termed “duress verticals,” for their proclivity to scams built to ensnare victims when they’re most vulnerable.
These bogus businesses flood local search results by setting up fake profiles in Google My Business (GMB), the free service that powers the business listings in Google Search and Maps. This dilutes search visibility for legitimate business listings, robbing them of potential customers, and puts users in a position to be scammed.
Google’s failure to take down fake business listings and verify real ones is a frustration for many business owners and marketers. Joe Youngblood, an SEO and digital marketer, has been vocal about the problems legitimate businesses face with Google My Business. “Hey@GoogleMyBiz still have several real businesses with suspended accounts, meanwhile fake spam companies with Virtual Office addresses are popping up everywhere. It’s been almost a full week, can you please respond to these??,” Youngblood tweeted this week.
The problem isn’t always as black and white as fake and real local listings, either. As digital marketer Itamar Blauer pointed out, real businesses are also stuffing keywords into their Google My Business profiles in order to rank higher on generic local searches (e.g., “oil change” or “personal injury lawyer”).
Google’s guidelines state, “Your name should reflect your business’ real-world name, as used consistently on your storefront, website, stationery, and as known to customers.” It also instructs businesses to include details like address and service area, business hours, and categories of the other sections of your business.
“The underlying concept of this is that there don’t seem to be consequences for keyword stuffing in GMB listings, as Optimise London have shown that even after Google accepted my edit – they simply added the keywords in again,” Blauer said.
The impact of this manipulation isn’t limited to local search results either. The screenshot below shows that, by adding “SEO Agency” to its business name in GMB, an agency managed to get featured in a knowledge panel for the generic search term “digital seo agency.”
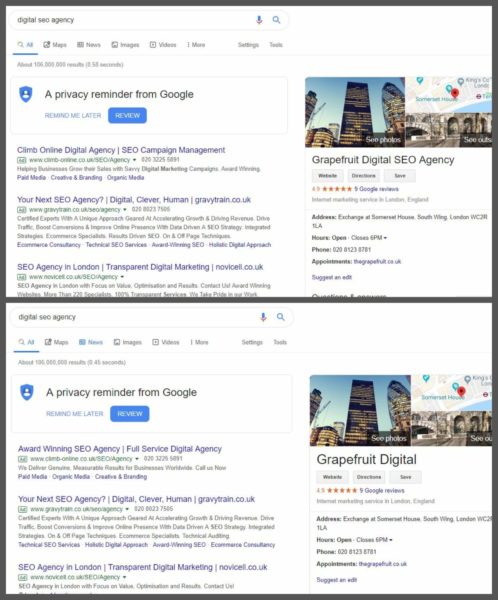
The top screenshot shows how an agency was able to gain a knowledge panel for the non-brand search term “digital seo agency” by putting “SEO Agency” in its GMB profile. Even after the spammy name was reported, the knowledge panel remained, as shown in the second screenshot.
“Now the knowledge graph picks up their GMB for ‘Digital SEO Agency,’ which shouldn’t be allowed and is only the case because of their GMB title,” Blauer explained. Even after the listing was corrected, the company’s listing remained in the knowledge panel, despite ranking seventh in the standard organic listings.
“Right now the name of the business has a huge impact, and fake listings just use target keywords, leading to massive gains,” Youngblood explained. Last year, he ran an experiment that revealed that on average, spamming or keyword stuffing the GMB business name helped a location improve by at least 9.53 ranking positions.
How Google got into this situation
Some marketers say Google didn’t take the problem of listing authenticity seriously enough from the start. “As those of us in the YP [yellow pages] industry watched Google enter into providing local business information, we thought they had quite a bit of hubris,” Chris Silver Smith, formerly a technical liaison for a deal between Superpages and Google Maps and now president and strategist at Argent Media, said.
“There was a naivete in much of their approach that translated into all sorts of goofs and errors over time. Instead of hiring people who were highly familiar with the issues inherent, they primarily hired computer science grads, fresh out of school, and treated the database with less seriousness at the beginning than should have been the case — far more priority was placed on the user experience than virtually anything else.”
Silver Smith also said that Google has over-emphasized having brick-and-mortar locations in their ranking algorithm — despite the fact that many service providers don’t need office space because they work on-site at their customers’ locations. According to Silver Smith, the heavy weighting of that factor makes it makes it more difficult for service providers that don’t need a physical location to achieve high rankings, ultimately incentivizing them to set up fake listings just to be represented equivalently to businesses with street addresses.
Google’s responses
In 2017, a Google-sponsored study by researchers from the University of California, San Diego concluded that just 0.5% of the local searches they looked at contained false listings. Search consultant Mike Blumenthal called the results “meaningless,” partially due to the limited and skewed data that Google provided. Danny Huang, the study’s lead author, who was also a paid Google intern at the time, acknowledged, “All I was doing was eyeballing in a scientific manner.”
Shortly after the WSJ article was published, Google emphasized in blog post its ongoing efforts to address Maps spam and scammers, saying it has taken down over three million fake business profiles, of which more than 90% were removed before they could be seen by users. It also stated that it is donating settlement funds from lawsuits against bad actors to organizations that educate consumers and businesses about fraud, and reiterated that users can flag profiles for removal.
The company added that it’s developing new ways — both manual and automated — to fight scammers, but kept specifics under wraps, explaining “we can’t share too many details about these efforts without running the risk of actually helping scammers find new ways to beat our systems—which defeats the purpose of all the work we do.”
The company has also signaled it may start charging for Google My Business features. In April, it sent a survey to some local businesses asking if they would be willing to pay a monthly subscription fee.
Google Maps carries approximately 11 million illegitimate local listings, with hundreds of thousands more getting created each month, the Wall Street Journal reported this week. These fake listings push real businesses further down the local search results, impacting their ability to reach customers and make unsuspecting users easy targets for scammers.
Google says it is aware of the problem and that it has plans to do more to combat spammers and scammers taking advantage of local listings. It’s not in the company’s interest to jeopardize user trust, yet as many marketers point out, it stands to profit as local businesses turn to paid ads to regain search visibility.
“Duress vertical” scams and spammy business names
First, a look at the problem. The majority of car repair, towing, electricians, contractors, attorneys, movers and other service categories aren’t located at the addresses shown in Google Maps, according to a survey of experts conducted by the WSJ. Internally at Google, the paper reprted, these categories are termed “duress verticals,” for their proclivity to scams built to ensnare victims when they’re most vulnerable.
These bogus businesses flood local search results by setting up fake profiles in Google My Business (GMB), the free service that powers the business listings in Google Search and Maps. This dilutes search visibility for legitimate business listings, robbing them of potential customers, and puts users in a position to be scammed.
Google’s failure to take down fake business listings and verify real ones is a frustration for many business owners and marketers. Joe Youngblood, an SEO and digital marketer, has been vocal about the problems legitimate businesses face with Google My Business. “Hey
The problem isn’t always as black and white as fake and real local listings, either. As digital marketer Itamar Blauer pointed out, real businesses are also stuffing keywords into their Google My Business profiles in order to rank higher on generic local searches (e.g., “oil change” or “personal injury lawyer”).
Google’s guidelines state, “Your name should reflect your business’ real-world name, as used consistently on your storefront, website, stationery, and as known to customers.” It also instructs businesses to include details like address and service area, business hours, and categories of the other sections of your business.
“The underlying concept of this is that there don’t seem to be consequences for keyword stuffing in GMB listings, as Optimise London have shown that even after Google accepted my edit – they simply added the keywords in again,” Blauer said.
The impact of this manipulation isn’t limited to local search results either. The screenshot below shows that, by adding “SEO Agency” to its business name in GMB, an agency managed to get featured in a knowledge panel for the generic search term “digital seo agency.”

The top screenshot shows how an agency was able to gain a knowledge panel for the non-brand search term “digital seo agency” by putting “SEO Agency” in its GMB profile. Even after the spammy name was reported, the knowledge panel remained, as shown in the second screenshot.
“Now the knowledge graph picks up their GMB for ‘Digital SEO Agency,’ which shouldn’t be allowed and is only the case because of their GMB title,” Blauer explained. Even after the listing was corrected, the company’s listing remained in the knowledge panel, despite ranking seventh in the standard organic listings.
“Right now the name of the business has a huge impact, and fake listings just use target keywords, leading to massive gains,” Youngblood explained. Last year, he ran an experiment that revealed that on average, spamming or keyword stuffing the GMB business name helped a location improve by at least 9.53 ranking positions.
How Google got into this situation
Some marketers say Google didn’t take the problem of listing authenticity seriously enough from the start. “As those of us in the YP [yellow pages] industry watched Google enter into providing local business information, we thought they had quite a bit of hubris,” Chris Silver Smith, formerly a technical liaison for a deal between Superpages and Google Maps and now president and strategist at Argent Media, said.
“There was a naivete in much of their approach that translated into all sorts of goofs and errors over time. Instead of hiring people who were highly familiar with the issues inherent, they primarily hired computer science grads, fresh out of school, and treated the database with less seriousness at the beginning than should have been the case — far more priority was placed on the user experience than virtually anything else.”
Silver Smith also said that Google has over-emphasized having brick-and-mortar locations in their ranking algorithm — despite the fact that many service providers don’t need office space because they work on-site at their customers’ locations. According to Silver Smith, the heavy weighting of that factor makes it makes it more difficult for service providers that don’t need a physical location to achieve high rankings, ultimately incentivizing them to set up fake listings just to be represented equivalently to businesses with street addresses.
Google’s responses
In 2017, a Google-sponsored study by researchers from the University of California, San Diego concluded that just 0.5% of the local searches they looked at contained false listings. Search consultant Mike Blumenthal called the results “meaningless,” partially due to the limited and skewed data that Google provided. Danny Huang, the study’s lead author, who was also a paid Google intern at the time, acknowledged, “All I was doing was eyeballing in a scientific manner.”
Shortly after the WSJ article was published, Google emphasized in blog post its ongoing efforts to address Maps spam and scammers, saying it has taken down over three million fake business profiles, of which more than 90% were removed before they could be seen by users. It also stated that it is donating settlement funds from lawsuits against bad actors to organizations that educate consumers and businesses about fraud, and reiterated that users can flag profiles for removal.
The company added that it’s developing new ways — both manual and automated — to fight scammers, but kept specifics under wraps, explaining “we can’t share too many details about these efforts without running the risk of actually helping scammers find new ways to beat our systems—which defeats the purpose of all the work we do.”
The company has also signaled it may start charging for Google My Business features. In April, it sent a survey to some local businesses asking if they would be willing to pay a monthly subscription fee.
